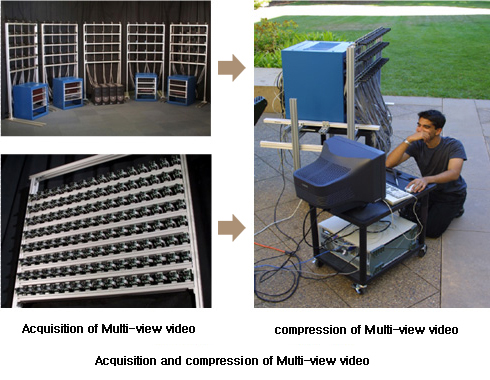
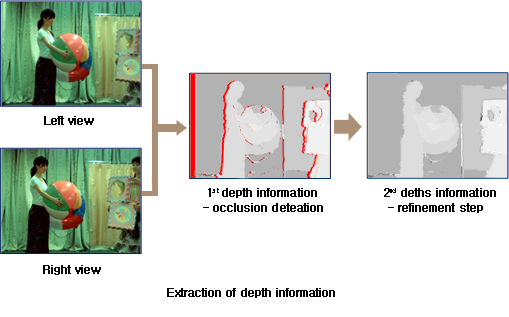
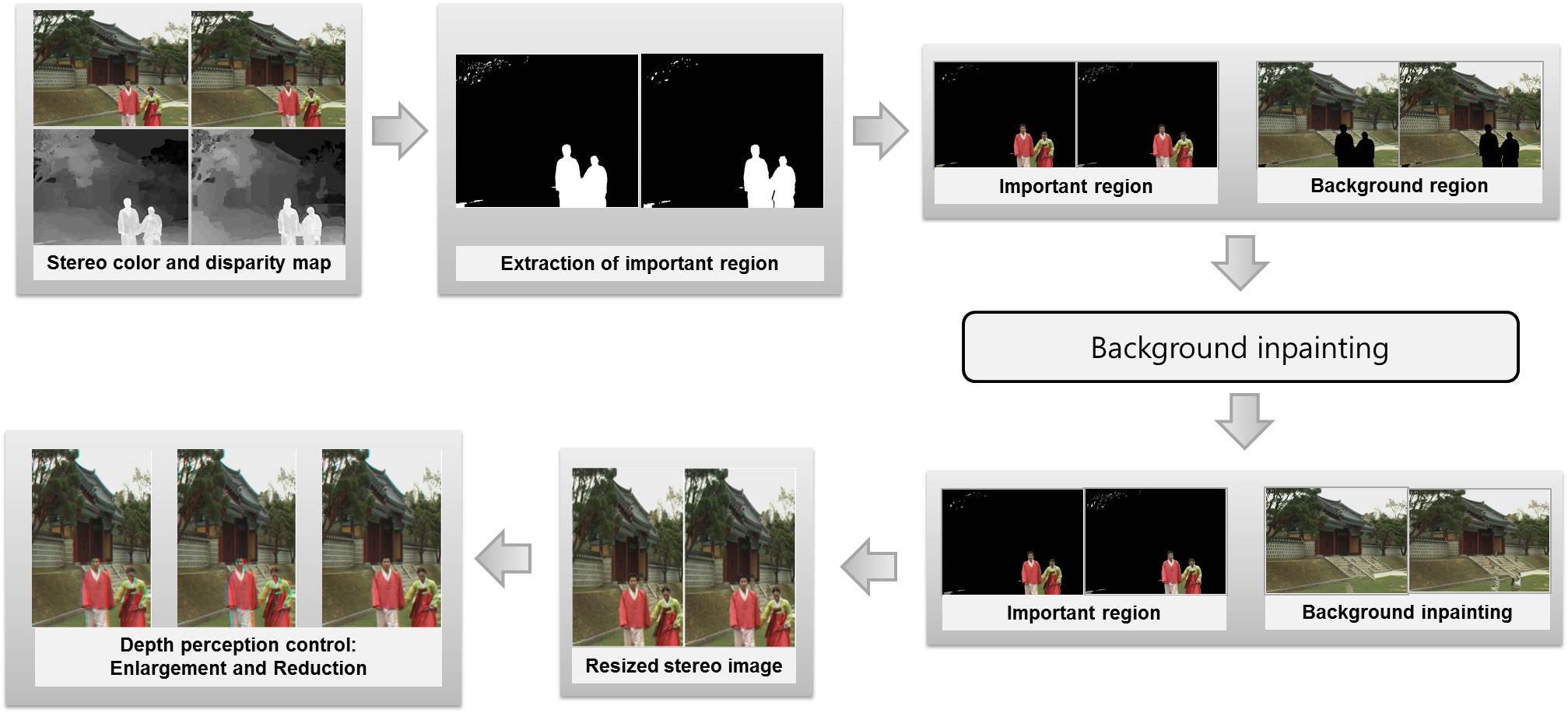
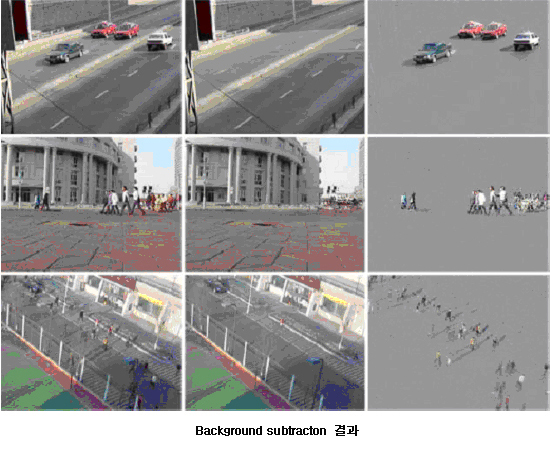
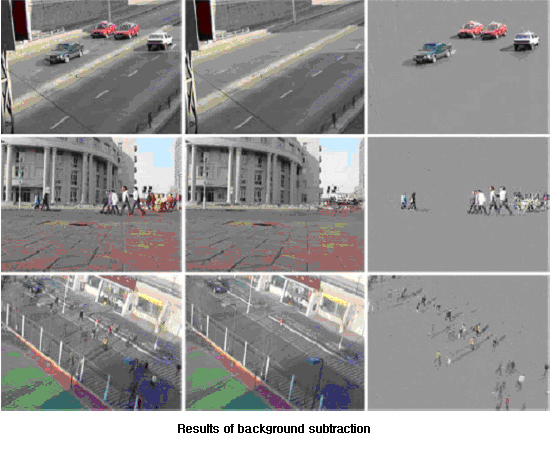
1. Background subtraction
전경의 물체를 배경으로부터 분리하는 것은 컴퓨터 비전과 영상처리에서 중요한 과정이다. 이러한 알고리즘은 감시 시스템(surveillance system), 물체 추적(object tracking) 및 교통 상황 관찰(traffic monitoring) 등의 다양한 컴퓨터 비전 응용의 첫 단계에 위치하게 된다. 전경 추출 알고리즘은 적은 복잡도를 가지면서 정확하게 동작하여야 한다. 배경에 대한 모델을 세우기 위해 색, 밝기, 지역 정보 등의 여러 특징들을 사용할 수 있다. 우리 연구실에서는 낮은 복잡도에 정확한 전경추출을 하기 위하여 다음과 같은 연구를 진행 하고 있다.
- 다양한 환경 조건하에서 강한 전경 추출 기법
- 하드웨어 구현을 위한 빠른 전경 추출 기법

2. Omni camera unwarping
비디오 감시 분야에서 넓은 영역을 관찰하는 것은 매우 중요하다. 넓은 영역을 관찰하기 위한 방법으로는 PTZ카메라를 이용하거나 여러 개의 카메라로 찍은 영상을 합성하는 방법이 있다. 또 다른 방법으로 전방위 카메라라는 360도 전 방향을 관찰할 수 있는 카메라를 사용할 수 있다. 그러나 전방위 카메라부터 획득된 영상은 렌즈나 거울의 모양에 따른 왜곡이 발생하므로 이렇게 발생한 왜곡을 효과적으로 펼 수 있는 방법이 필요하다. 본 연구실에서는 이와 관련하여 다음과 같은 연구를 진행하고 있다.
- 전방위 카메라를 이용한 감시 및 추적에 관한 연구
- 전방위 카메라의 자동-칼리브레이션에 관한 연구
- 전방위 카메라의 영상 왜곡을 줄이는 연구

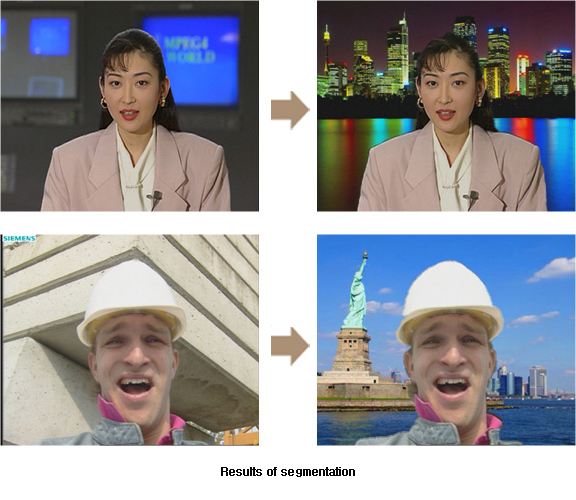
3. Bi-layer segmentation
본 연구실에서는 실시간 객체 분할 알고리즘을 개발하고 있으며, 이는 동영상으로부터 객체와 배경을 분할한다. 먼저 객체와 배경에 대한 컬러 확률 모델을 만들기 위해 첫 프레임은 사용자의 반응을 통해 분할한다. 그리고 각 프레임에 대해 시공간적 연관성을 이용하여 객체의 실루엣이 되는 연관틀을 만든다. 마지막으로 컬러, 연관성 그리고 스무드 항을 바탕으로 한 에너지 최소화를 통해 객체를 분할한다. 본 연구실에서 제안하는 알고리즘은 실시간으로 정확한 객체를 추출할 수 있으며, 심지어는 불안정한 카메라 움직임하에서도 작동한다. 객체를 분할한 뒤에 사용자는 배경을 아래와 같이 다른 그림으로 대체할 수 있다. 이러한 방법은 모바일 화상통신에서 사용자가 배경을 공개하고 싶지 않을 때 사생활을 보호할 수 있는 방법이다.

1. Background subtraction
Segmenting foreground objects from the background is an important task in computer vision and image processing. It is employed as the first stage of many computer vision applications, such as video surveillance, object tracking, and traffic monitoring. It should be performed reliably with low complexity. Several features, such as color, brightness and spatial information, can be used to build a background model. In MCL, to achieve reliable background subtraction at a low complexity, we are researching
- Robust background subtraction algorithms in various environmental conditions
- Fast background subtraction algorithms for hardware implementation

2. Bi-layer segmentation
We are developing a real-time video segmentation algorithm, which can extract objects from video sequences even with non-stationary backgrounds. First, we segment the first frame into an object and a background interactively to build the probability density functions of colors in the object and the background. Then, for each subsequent frame, we construct a coherence strip, which is likely to contain the object contour, by exploiting spatio-temporal correlations. Finally, we perform the segmentation by minimizing an energy function, which is composed of color, coherence, and smoothness terms. The proposed algorithm provides accurate segmentation results in real-time, even though video sequences contain unstable camera motions. After the segmentation, a user can substitute the background with another one as shown in the following figure. This can be used to protect privacy in mobile video communications, when a user does not want to reveal the background.

3. Omni camera unwarping
In video surveillance, it is desirable to capture a larger region with a camera. To cover a huge region, we can use a PTZ camera or merge images from several cameras. An alternative approach is to use an omni-directional camera, which can observe 360 degrees of angle. However, image, captured by omni-cameras, are distorted by the geometry of lens and mirrors. It is hence necessary to unwarp the distortions. We are working on
- Surveillance and tracking using omni-directional cameras
- Automatic calibration of omni-directional cameras
- Reduction of distortions in the unwarping procedure