Project Attachment Slider
This is a portfolio page template which pulls in posts and all their image attachments. If there is more than one, it automatically builds the image slider.
You can control the source categories and posts per page in the theme settings page or on a per-page basis using custom fields!
디지털 영상의 동적 영역(Dynamic Range)은 영상 내에서 가장 밝은 화소값과 가장 어두운 화소값의 비율로 정의한다. 일반적인 디지털 카메라 및 모니터는 2의 차수 크기의 동적 영역을 다룰 수 있는데 반해, 실제 인간의 시각 인지 시스템(HVS)은 5 이상 차수 크기의 동적 영역을 인지할 수 있다. 따라서, 기존의 영상 장치는 인간이 인지하는 영상을 그대로 획득(capture) 또는 표현(display) 할 수 없다. 이처럼 기존의 영상 장치가 다룰 수 있는 것보다 큰 동적 영역을 갖는 영상의 필요성이 대두되며, 이러한 영상을 높은 동적 영역(High Dynamic Range, HDR) 영상이라고 한다. HDR 영상은 디스플레이 장치가 표현할 수 있는 영상이 아닌 인간이 인지하는 그대로의 영상을 획득할 수 있어, 기존의 낮은 동적 영역(Low Dynamic Range, LDR) 영상에 비해 더 사실적인 장면을 나타낼 수 있다. 이처럼 많은 장점을 가지고 있는 만큼, 디지털 영상 장치의 발전과 더불어 가까운 미래에는 HDR 영상의 사용이 일반화 것으로 예상된다. 본 연구실에서는 이와 관련하여 다음과 같은 연구를 진행하고 있다.
- HDR 영상 및 동영상 획득 알고리즘
- HDR 영상 및 동영상 압축에 관한 연구
- HDR 영상을 기존의 LDR 디스플레이 장치에 표시하기 위한 알고리즘
 The dynamic range of a digital image is defined as the ratio of the intensities between the brightest pixel and the darkest pixel. While the dynamic ranges of conventional display devices are less than two orders of magnitude, real world scenes have much higher dynamic ranges. Also, human eyes can perceive more than six orders of magnitude via adaptation. Images that have higher dynamic ranges than conventional display devices are called high dynamic range (HDR) images. As the HDR images represent what human perceives rather than what display devices can express, they can capture real gamut more faithfully than low dynamic range (LDR) devices. The recent advance of sensor technology makes it possible to record the full dynamic range of a scene in a single shot. It is also expected that general still or video cameras will be able to capture HDR scenes directly in near future. We are doing researches on
The dynamic range of a digital image is defined as the ratio of the intensities between the brightest pixel and the darkest pixel. While the dynamic ranges of conventional display devices are less than two orders of magnitude, real world scenes have much higher dynamic ranges. Also, human eyes can perceive more than six orders of magnitude via adaptation. Images that have higher dynamic ranges than conventional display devices are called high dynamic range (HDR) images. As the HDR images represent what human perceives rather than what display devices can express, they can capture real gamut more faithfully than low dynamic range (LDR) devices. The recent advance of sensor technology makes it possible to record the full dynamic range of a scene in a single shot. It is also expected that general still or video cameras will be able to capture HDR scenes directly in near future. We are doing researches on
- Capturing of HDR images and videos
- Compression of HDR images and videos
- Displaying HDR images on LDR devices

디스플레이 크기와 인간 시각 시스템의 3차원 인식 메커니즘을 고려하여 사용자에게 편안한 입체감을 제공할 수 있는 스테레오 영상의 크기 조정 및 디스패리티 재구성 기법을 개발한다. 첫째, 입력 영상의 크기를, 스테레오 영상의 일치 정합(correspondence matching) 관계를 보존하면서, 전경과 배경에 따라 적응적으로 조정하는 크기 조정 기법을 개발한다. 우선 스테레오 정합 알고리즘을 이용하여 획득된 디스패리티 정보와, 그래디언트(gradient), 텍스쳐(texture) 등과 같은 영상 특성으로부터 입력 영상의 중요도 지도(importance map)을 추출한다. 그리고 디스패리티 정보와 중요도 지도에 따라 좌시점과 우시점에 해당하는 영상의 크기를 조정할 때 중요한 영역의 크기는 보존하고 덜 중요한 영역을 줄임으로써 원하는 크기의 출력 스테레오 영상을 구한다. 이러한 크기 조정 과정에서 일치 정합 관계와 폐색 영역(occluded regions)을 고려함으로써 출력 영상의 3차원 깊이 정보가 충실히 보존될 수 있도록 한다. 그러나 크기 조정은 필연적으로 디스패리티 정보의 변경과 비-중요 영역의 축소를 초래한다. 이러한 정보의 왜곡을 에너지 함수로 정의하고 최소화함으로써 최적 화질의 출력 영상을 얻는다. 둘째, 디스패리티 정보를 조정하여 시청자에게 편안한 3차원 시청거리를 제공하는 스테레오 영상의 디스패리티 재구성 기법을 개발한다. 시청자가 자연스러운 입체감을 느낄 수 있는 거리는 제한되어 있으며 일반적으로 화면의 크기에 비례한다. 따라서 스테레오 영상의 크기가 변경되거나 화면의 크기가 다른 출력 장치를 통해 시청할 경우, 최적의 3차원 시청 거리 또한 변경될 수 밖에 없다. 이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해서 본 연구에서는 영상 크기의 변화에 상관없이 균일한 3차원 시청 거리를 제공할 수 있는 디스패리티 재구성 기법을 개발한다. 관련과제 – IT/SW 창의연구과정-한국마이크로소프트: Stereoscopic Image Retargeting and Disparity Remapping for Adaptation of 3D Video Contents for Various Display Devices
- 디스패리티를 이용한 중요 영역 추출 알고리즘
- 스테레오 이미지 인페인팅 알고리즘
- 디스패리티 리맵핑을 통한 입체감 조정 기법
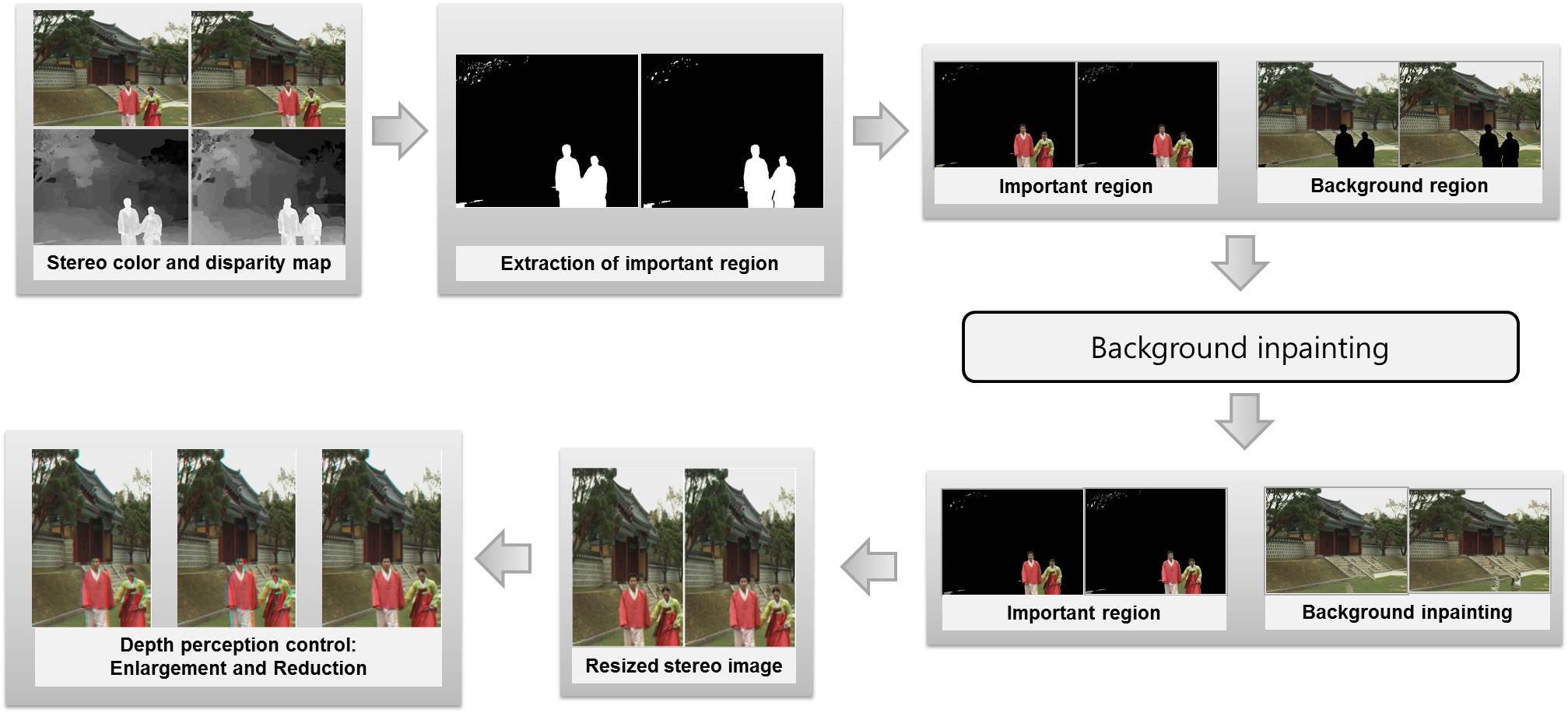
We develop stereo image resizing and disparity remapping technique which can provide comfortable depth perception, while a display size and human visual recognition system are considered. First, we develop stereo image retargeting method, which resize the image size according to important region and background while a correspondence matching relation is preserved. First, we extract importance map using image characteristics, such as gradient and texture, and a disparity data which is given. Then, we resize left and right image while preserve important regions and distort background regions until fitting target image size. Moreover, we consider occluded regions and correspondence match relation to preserve depth perception when resizing stereo image. Second, we develop disparity remapping method controlling depth perception to provide comfortable 3D contents viewing. A viewing distance, which a viewer can feel comfortable depth perception at, is limited. Therefore, if image or display size is changed, the viewing distance should be changed. To solve this problem, we develop disparity remapping method, which provide comfortable depth perception without a limitation of viewing distance even though image or display size is changed. (related research project: IT/SW Microsoft Research Asia: Stereoscopic Image Retargeting and Disparity Remapping for Adaptation of 3D Video Contents for Various Display Devices) We are doing researches on
- Extraction of importance regions based disparity data
- Inpainting stereo image
- Ramapping disparity data and controlling depth perception







